· bitkarrot · 9 min read
The Unwritten Rules of FOSS

The Unwritten Rules of Open Source Development: Nurturing a Collaborative Ecosystem
Introduction
Open source development has revolutionized the way software is created, distributed, and maintained. It thrives on principles of transparency, collaboration, and community-driven innovation. Beyond the formal licenses and coding conventions, there exists a set of unwritten rules that govern the behavior and interactions within this dynamic ecosystem. These unwritten rules are the glue that holds the open source community together, fostering an environment of trust, respect, and mutual growth.
We will explore the following:
- The Why behind open source development.
- Why should I contribute code for free?
- Private vs. Public Open Source Models
- Some Do’s and Don’ts when collaborating remotely
The Why behind open source development.
Voluntary Contribution and Passion-Driven Work
One of the foundational unwritten rules of open source development is the spirit of voluntary contribution. Developers engage in open source projects out of sheer passion and the desire to make a positive impact on the community. This voluntary nature underpins the collaborative ethos of open source, creating a space where individuals come together to build something greater than themselves.
Transparent Communication
Clear and transparent communication is paramount in open source development. This includes providing comprehensive documentation, maintaining open channels for discussion, and offering constructive feedback. Developers should be responsive and willing to share their knowledge to foster a culture of learning and growth within the community.
Respect for Diverse Perspectives
Open source development transcends geographical, cultural, and linguistic boundaries. Embracing diversity in all its forms is not only an unwritten rule but also a strength of the open source community. Respecting diverse perspectives fosters creativity and ensures that solutions are robust, adaptable, and inclusive.
Collaboration Over Competition
In open source, the emphasis lies on collaboration rather than competition. Developers work together, pooling their expertise to create software that benefits the broader community. This cooperative mindset encourages the sharing of ideas, code, and knowledge, leading to the collective advancement of technology.
Recognition and Attribution
Acknowledging the contributions of individuals is a cornerstone of open source development. Every line of code, bug report, or documentation edit represents a valuable contribution. Proper attribution not only recognizes the effort put in but also motivates individuals to continue their valuable work.
Code of Conduct and Inclusive Environment
While not always explicitly stated, an unwritten rule within open source development is the adherence to a code of conduct that ensures a safe, respectful, and inclusive environment for all participants. This promotes a sense of belonging and encourages a diverse range of individuals to engage and contribute.
Pragmatic Problem Solving
Open source development places a premium on practical, real-world problem-solving. Developers focus on creating solutions that are effective, efficient, and adaptable to meet the needs of a wide range of users. This pragmatic approach leads to the development of robust, user-friendly software.
Long-term Commitment and Sustainability
Open source projects often require long-term commitment for their success and sustainability. Developers are encouraged to support and maintain their projects, ensuring that they remain relevant and continue to serve the community over time.
Why should I contribute code for free? What are the real benefits here?
Contributing code to open source projects without monetary compensation may seem counterintuitive at first glance, but there are several compelling reasons why individuals choose to participate in this collaborative ecosystem. Here are some of the key benefits:
Skill Development and Learning Opportunities:
Engaging in open source allows you to hone your coding skills and gain hands-on experience with real-world projects. It offers a practical learning environment where you can work on diverse and challenging tasks.
Building a Portfolio:
Open source contributions serve as a tangible demonstration of your skills and expertise. They can be showcased in your portfolio or resume, making you more attractive to potential employers or clients.
Networking and Community Engagement:
Participating in open source introduces you to a global community of developers, designers, and enthusiasts. It provides opportunities to connect with like-minded individuals, attend conferences, and participate in discussions that can lead to valuable professional relationships.
Exposure to Best Practices and Coding Standards:
Open source projects often adhere to high-quality coding standards and best practices. By contributing, you learn from experienced developers and gain insights into industry-standard methodologies.
Solving Real-world Problems:
Open source projects often address real-world issues faced by users and organizations. By contributing, you have the opportunity to create solutions that have a direct impact on the community and society at large.
Contributing to a Larger Cause:
Many open source projects serve a broader mission, such as promoting accessibility, inclusivity, or advancing technology in a specific domain. Contributing allows you to be part of a collective effort to make a positive impact.
Personal Fulfillment and Satisfaction:
Knowing that your contributions are used by a global community can be immensely satisfying. It provides a sense of accomplishment and purpose, as you witness the tangible results of your efforts.
Exposure to Cutting-edge Technologies:
Open source projects often utilize innovative technologies and tools. By participating, you have the opportunity to work with state-of-the-art software, frameworks, and libraries, which can enhance your knowledge and skill set.
Access to Feedback and Peer Review:
Open source contributions undergo peer review, allowing you to receive feedback on your code. This iterative process helps you improve your coding practices and learn from experienced developers.
Potential for Future Opportunities:
Active involvement in open source can lead to job opportunities, consulting gigs, or even entrepreneurial ventures. Many companies value candidates with a strong open source track record.
While open source contributions may not offer immediate financial compensation, the benefits mentioned above can lead to long-term personal and professional growth, as well as open doors to exciting opportunities in the tech industry. It’s a testament to the vibrant and collaborative nature of the open source community.
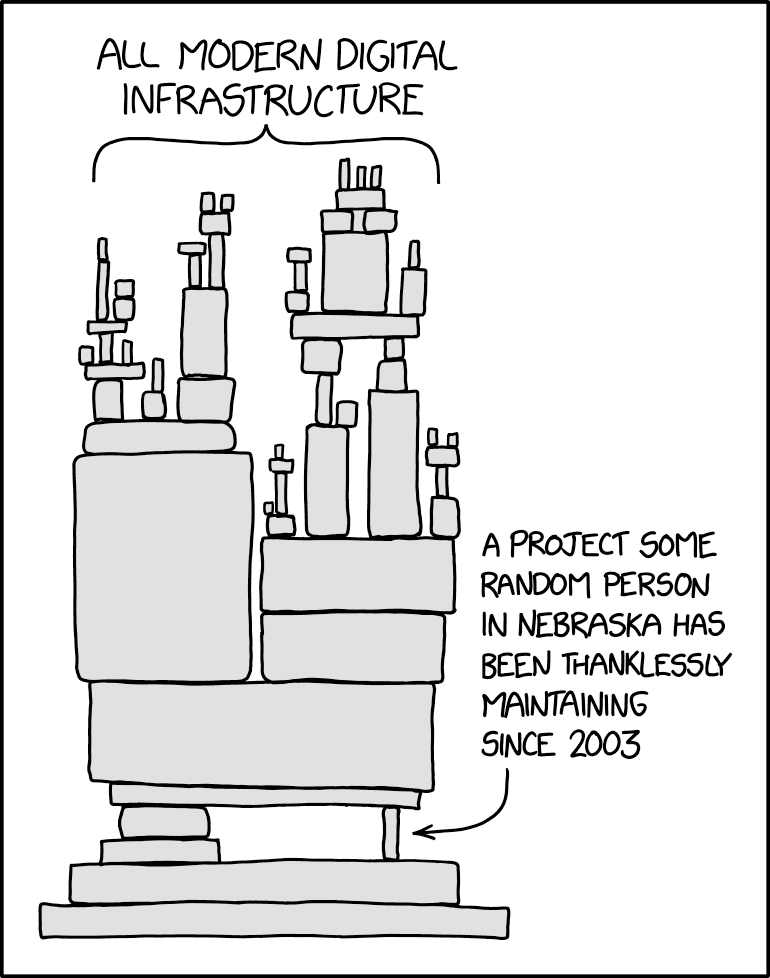
Private vs. Public Open Source Models:
Private Open Source Model:
In a private open source model, a company develops software using open source methodologies but keeps the codebase private. They may choose to selectively release parts of their code as open source, contribute to existing open source projects, or use open source software as part of their internal development process. Examples of companies following this model include Apple and Microsoft.
Public Open Source Model:
Companies following the public open source model develop their software entirely in the open, meaning that the source code is available for anyone to view, use, modify, and distribute. They often have a community of contributors from both within and outside the company. Examples of companies following this model include Red Hat (acquired by IBM) and Canonical (the company behind Ubuntu).
Examples of Successful Companies Fully Embracing Open Source:
Red Hat (now part of IBM):
Red Hat is a pioneer in the open source industry. It provides enterprise solutions, including the popular Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) operating system. Their business model is based on providing support, training, and services around their open source products.
Canonical (Ubuntu):
Canonical is the company behind Ubuntu, one of the most widely used Linux distributions. While Ubuntu is free and open source, Canonical offers additional services like enterprise support, cloud management, and consulting.
Automattic (WordPress):
WordPress, the popular content management system (CMS), is an open source project managed by Automattic. They offer various services including hosting, premium themes, and plugins.
Elastic:
Elastic develops the Elastic Stack, which includes Elasticsearch, Kibana, Logstash, and Beats. These tools are widely used for search, logging, monitoring, and analytics. While the core software is open source, Elastic offers additional features and services under a commercial license.
MongoDB:
MongoDB is a widely used NoSQL database. MongoDB Inc. offers a dual licensing model. The core database is open source, but they also provide an enterprise version with additional features and support.
GitLab:
GitLab provides a complete DevOps platform that covers source code management, CI/CD, monitoring, and more. The core GitLab software is open source, and they offer additional features through a commercial offering.
These examples illustrate that a successful business model can be built around open source software. Companies can provide value-added services, support, and premium features while still maintaining a strong commitment to open source principles.
In summary, the open source model has become a significant and sustainable approach for many successful companies. It not only fosters innovation but also provides opportunities for community collaboration and a means to deliver high-quality software to a global audience.
What are some Do’s and Don’ts when collaborating remotely?
Collaborating remotely requires a set of best practices to ensure effective communication, productivity, and a positive working environment. Here are some Do’s and Don’ts for remote collaboration:
Do’s:
Establish Clear Communication Channels:
Use a combination of messaging apps, video conferencing, email, and project management tools to facilitate clear and timely communication.
Set Clear Expectations and Deadlines:
Clearly define tasks, responsibilities, and project timelines to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Regular Check-ins and Updates:
Schedule regular team meetings or stand-ups to discuss progress, challenges, and upcoming tasks.
Use Collaborative Tools:
Utilize tools like shared documents, version control systems, and project management platforms to facilitate collaborative work.
Provide Constructive Feedback:
Give feedback that is specific, actionable, and respectful. Focus on solutions rather than just pointing out problems.
Respect Different Time Zones:
Be mindful of team members’ time zones and try to schedule meetings and deadlines that are reasonable for everyone.
Document Decisions and Agreements:
Keep a record of discussions, decisions, and agreements made during meetings to avoid misunderstandings.
Encourage and Acknowledge Contributions:
Celebrate achievements and acknowledge the efforts of team members. Recognizing their contributions boosts morale and motivation.
Don’ts:
Don’t Overlook Team Building:
Even in a remote setting, team building activities, virtual social events, and informal chats are important for building trust and camaraderie.
Don’t Micromanage:
Avoid excessive monitoring and micromanagement. Trust team members to complete their tasks independently and provide support when needed.
Don’t Assume Availability:
Respect that team members may have different schedules and commitments. Avoid expecting instant responses to messages or requests.
Don’t Neglect Documentation:
Ensure that processes, guidelines, and important information are documented and easily accessible to all team members.
Don’t Avoid Difficult Conversations:
Address conflicts or challenges promptly and professionally. Ignoring issues can lead to bigger problems down the line.
Don’t Ignore Well-being:
Consider the well-being of team members. Encourage breaks, promote work-life balance, and provide resources for mental health support.
Don’t Rely Solely on Text-Based Communication:
Incorporate video calls or voice chats when needed. Non-verbal cues and tone of voice can convey information and emotions that text alone may not capture.
Don’t Forget About Security:
Ensure that sensitive information is handled securely, and use encryption and secure channels for confidential discussions.
By adhering to these Do’s and Don’ts, you can create a productive and supportive remote working environment that enables effective collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location.